Miscellaneous のバックアップ(No.1)
- バックアップ一覧
- 差分 を表示
- 現在との差分 を表示
- ソース を表示
- Miscellaneous へ行く。
- 1 (2009-01-21 (水) 18:12:32)
- 2 (2014-08-22 (金) 18:39:00)
Since silicon is quite abundant in the earth's crust, its utilization in organic synthesis, material science, and medicinal science is highly desirable. We have developed new catalytic silylation reactions on the basis of activation of the silicon-containing σ-bond by transition metal catalysts.
Bis-Silylation
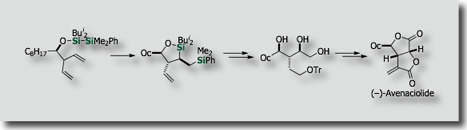
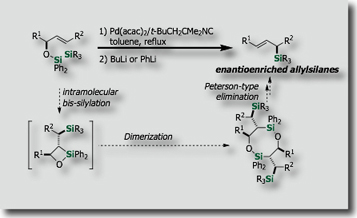
For instance, intramolecular bis-silylations have been developed on the basis of our finding on new palladium catalysts, i.e., palladium-isocyanide catalysts [Ref .1], for the activation of the Si-Si bond. The intramolecular reactions enabled the synthesis of enantioenriched allylsilanes [Ref. 2], allenylsilanes [Ref. 3] and polyols [Ref. 4] in stereoselective fashions.
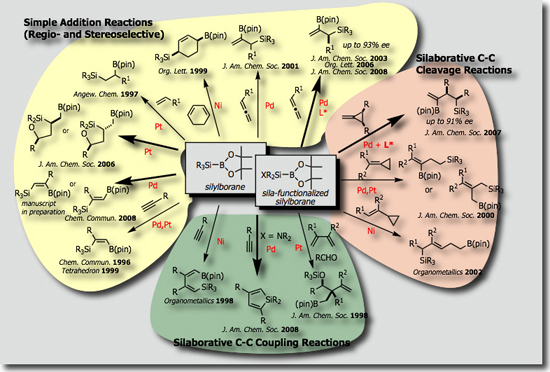
Silaborations
We established that the Si-B bond shows remarkable selectivity and reactivity in the presence of transition metal catalysts [Ref. 5]. We could establish a variety of catalytic reactions involving (1) simple addition reactions (silaborations) [Ref. 6], (2) silaborative C–C coupling reactions [Ref. 7], and (3) silaborative cleavage of C-C bonds in small rings [Ref. 8]. In addition, recent success in synthesizing Si-functionalized silylboranes [Ref. 9, see also Ref. 10] allowed us to find that (dialkylamino)diorganosilylboranes serves as a synthetic equivalent of “silylene” [Ref. 11]. Typical catalytic reactions we have so far developed are shown below.
References
- Ref. 1
- Palladium-Catalyzed Insertion of Isocyanides into the Silicon-Silicon Linkages of Oligosilanes Y. Ito, M. Suginome, T. Matsuura, M. Murakami, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 8899-8908, 10.1021/ja00023a043
- Palladium(II) Acetate–tert-Alkyl Isocyanide as a Highly Efficient Catalyst for the Inter- and Intramolecular Bis-silylation of Carbon-Carbon Triple Bonds Y. Ito, M. Suginome, M. Murakami, J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 1948-1951, 10.1021/jo00005a055
- Intramolecular Bis-silylation of Carbon-Carbon Double Bonds Leading to Stereoselective Synthesis of 1,2,4-Triols M. Murakami, P. G. Andersson, M. Suginome, Y. Ito, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 3987-3988, 10.1021/ja00010a049
- Stereoselective Intramolecular Bis-Silylation of Alkenes Promoted by Palladium-Isocyanide Catalyst Leading to Polyol Synthesis M. Murakami, M. Suginome, K. Fujimoto, H. Nakamura, P. G. Andersson, Y. Ito, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 6487-6498, 10.1021/ja00068a003
- Synthesis and Structure of a Nontwisted Tetrakis(organosilyl)ethenes M. Murakami, M. Suginome, K. Fujimoto, Y. Ito, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 1993, 32, 1473-1475, 10.1002/anie.199314731, Angew. Chem. 1993, 105, 1542-1544, 10.1002/ange.19931051041
- Novel Activation of Two Si–Si σ-Bonds in a Molecule by tert-Alkyl Isocyanide–Palladium Complexes M. Suginome, H. Oike, Y. Ito, Organometallics 1994, 13, 4148-4150, 10.1021/om00023a009
- Macrocycles with Regularly Arranged Si–Si Bonds: Ring-Enlargement Oligomerization of Cyclic Disilanes via Palladium-Catalyzed Si-Si σ-Bond Metathesis. M. Suginome, H. Oike, Y. Ito, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 1665-1666, 10.1021/ja00110a034
- Reactions of Si–Si σ-Bonds with Bis(t-alkyl isocyanide)palladium(0) Complexes. Synthesis and Reactions of Cyclic Bis(organosilyl)palladium Complexes [Headline Article] M. Suginome, H. Oike, S.-S. Park, Y. Ito, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1996, 69, 289–299, 10.1246/bcsj.69.289
- Reactions of a Spiro Trisilane with Palladium Complexes: Synthesis and Structure of Tris(organosilyl))Cp Pd(IV) and Bis(organosilyl)(μ-organosilylene)Pd2(II) Complexes. M. Suginome, Y. Kato, N. Takeda, H. Oike, Y. Ito, Organometallics 1998, 17, 495-497, 10.1021/om9710778
- Ref. 2
- New Synthesis of (E)-Allylsilanes with High Enantiopurity via Diastereoselective Intramolecular Bis-Silylation of Chiral Allylic Alcohols M. Suginome, A. Matsumoto, Y. Ito, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 3061–3062, 10.1021/ja954251x
- Synthesis of Highly Enantio-enriched Allylsilanes via Palladium-catalyzed Intramolecular Bis-Silylation. Determination of the Enantiomeric Excesses through Regio- and Stereoselective Hydroboration with 9-BBN. M. Suginome, T. Iwanami, A. Matsumoto, Y. Ito, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 1997, 8, 859-862, 10.1016/S0957-4166(97)00073-6
- Stereoselective Cyclization of Highly Enantio-Enriched Allylsilanes with Aldehydes via Acetal Formation: New Asymmetric Access to Tetrahydropyrans and Piperidines M. Suginome, T. Iwanami, Y. Ito, J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 6096-6097, 10.1021/jo981173y
- Asymmetric Synthesis of 2,3-Disubstituted Oxepanes via Acetalization-Cyclization of an Enantioenriched Functionalized Allylsilane with Aldehydes M. Suginome, T. Iwanami, Y. Ito, Chem. Commun. 1999, 2537-2538, 10.1039/a908603j
- Asymmetric Synthesis of Cyclic Alkenes via Cyclization of Enantioenriched Allylsilanes M. Suginome, T. Iwanami, A. Yamamoto, and Y. Ito, Synlett, 2001, 1042-1045, 10.1055/s-2001-14656
- Solid-Phase Synthesis and Asymmetric Reactions of Polymer-Supported Highly Enantioenriched Allylsilanes M. Suginome, T. Iwanami, and Y. Ito, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 4356-4357, 10.1021/ja005865r
- Stereoselective Synthesis of Highly Enantioenriched (E)-Allylsilanes by Palladium-Catalyzed Intramolecular Bis-Silylation: 1,3-Chirality Transfer and Enantienrichment via Dimer Formation M. Suginome, T. Iwanami, Y. Ohmori, A. Matsumoto, Y. Ito, Chem. Eur. J., 2005, 11, 2954-2965, 10.1002/chem.200401031
- Ref. 3
- Palladium-Catalyzed Intramolecular Bis–Silylation of Propargylic Alcohols: A New Stereospecific Access to Chiral Allenylsilanes M. Suginome, A. Matsumoto, Y. Ito, J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 4884-4885, 10.1021/jo960778w
- Ref. 4
- Diastereoselective Intramolecular Bis-Silylation of a Carbon-Carbon Double Bond. A Highly Stereocontrolled Synthesis of (-)-Avenaciolide M. Suginome, Y. Yamamoto, K. Fujii, Y. Ito, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 9608–9609, 10.1021/10.1021/ja00142a047
- Intramolecular Bis-Silylation of Alkenes Catalyzed by Palladium(0) tert-alkyl isocyanide Complex. Stereoselective Synthesis of Polyols Y. Ito, M. Suginome, Pure Appl. Chem. 1996, 68, 505-508, 10.1351/pac199668030505
- Ref. 5
- Silylboranes as New Tools in Organic Synthesis T. Ohmura, M. Suginome, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. submitted.
- Ref. 6
- Regio- and Stereoselective Silaboration of Alkynes Catalyzed by Palladium and Platinum Complexes M. Suginome, H. Nakamura, Y. Ito, Chem. Commun., 1996, 2777–2778, 10.1039/CC9960002777
- Platinum-catalyzed Regioselective Silaboration of Alkenes. M. Suginome, H. Nakamura, Y. Ito, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1997, 36, 2516-2518, 10.1002/anie.199725161, Angew. Chem. 1997, 109, 2627-2628, 10.1002/ange.19971092237
- Regio- and Stereoselective Synthesis of (Z)-β-Silylalkenylboranes by Silaboration of Alkynes Catalyzed by Palladium and Platinum Complexes M. Suginome, T. Matsuda, H. Nakamura, Y. Ito, Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 8787-8800, 10.1016/S0040-4020(99)00444-5
- Highly Regioselective Silaboration of 3-Substituted 1,2-Dienes Catalyzed by Palladium/2,6-Xylyl Isocyanide M. Suginome, Y. Ohmori, Y. Ito, Synlett 1999, 1567-1568, 10.1055/s-1999-2917
- Stereoselective 1,4-Silaboration of 1,3-Dienes Catalyzed by Nickel Complexes M. Suginome, T. Matsuda, T. Yoshimoto, Y. Ito, Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 1567-1569, 10.1021/ol990908y
- Synthesis of (Boryl)(silyl)iminomethanes by Insertion of Isonitriles into Silicon-Boron Bonds M. Suginome, T. Fukuda, H. Nakamura, Y. Ito, Organometallics 2000, 19, 719-721, 10.1021/om9909136
- Palladium-Catalyzed Regioselective Silaboration of 1,2-Dienes M. Suginome, Y. Ohmori, Y. Ito, J. Organomet. Chem. 2000, 611, 403-413 (Special issue: The Chemistry of Interelement Linkage), 10.1016/S0022-328X(00)00472-1
- β-Borylallylsilanes as a New Tool for Convenient Synthesis of Alkenylboranes M. Suginome, Y. Ohmori, and Y. Ito, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 4601-4602, 10.1021/ja0058381
- Stereoselective construction of trans-1,2-benzooxadecaline frameworks by three-component cascade reactions of an α-phenethyl-β-borylallylsilane with aldehydes M. Suginome, Y. Ohmori, Y. Ito, Chem. Commun. 2001, 1090-1091, 10.1039/b102613p
- Enantioface-Selective Palladium-Catalyzed Silaboration of Allenes via Double Asymmetric Induction M. Suginome, T. Ohmura, Y. Miyake, S. Mitani, Y. Ito, M. Murakami, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 11174-11175, 10.1021/ja0368958
- The Asymmetric Silaboration of Terminal Allenes Bearingα-Stereogenic Centers: Stereoselection Based on “Reagent Control” T. Ohmura, M. Suginome, Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 2503–2506, 10.1021/ol060666j
- Palladium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Silaboration of Allenes T. Ohmura, H. Taniguchi, M. Suginome, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 13682-13683, 10.1021/ja063934h
- Ligand-Controlled, Complementary Stereoselectivity in the Platinum-Catalyzed Intramolecular Silaboration of Alkenes T. Ohmura, H. Furukawa, M. Suginome, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 13366-13367, 10.1021/ja065588+
- A Mechanism for the Palladium–Catalyzed Regioselective Silaboration of Allene: A Theoretical Study Y. Abe, K. Kuramoto, M. Ehara, H. Nakatsuji, M. Suginome, M. Murakami, Y. Ito, Organometallics 2008, 27, 1736-1742, 10.1021/om070110f
- Ref. 7
- Platinum-Catalyzed Silaborative Coupling of 1,3-Dienes to Aldehydes: Regio- and Stereoselective Allylation with Dienes through Allylic Platinum Intermediates M. Suginome, H. Nakamura, T. Matsuda, Y. Ito, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 4248-4249, 10.1021/ja980373o
- Nickel-Catalyzed Silaborative Dimerization of Alkynes M. Suginome, T. Matsuda, Y. Ito, Organometallics 1998, 17, 5233-5235, 10.1021/om9807250
- Ref. 8
- Palladium- and Platinum-Catalyzed Silaboration of Methylenecyclopropanes through Selective Proximal or Distal C-C Bond Cleavage M. Suginome, T. Matsuda, and Y. Ito, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 11015-11016, 10.1021/ja002885k
- Nickel-Catalyzed Silaboration of Small-Ring Vinylcycloalkanes: Regio- and Stereoselective (E)-Allylsilane Formation via C-C Bond Cleavage. M. Suginome, T. Matsuda, T. Yoshimoto, Y. Ito, Organometallics 2002, 21, 1537-1539, 10.1021/om020007k
- Palladium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Silaborative C–C Cleavage of meso-Methylenecyclopropanes T. Ohmura, H. Taniguchi, Yoshiyuki Kondo, M. Suginome, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 3518-3519, 10.1021/ja0703170
- Ref. 9
- Synthesis of Silylboronic Acid Esters Functionalized on Silicon T. Ohmura, K. Masuda, Hideki Furukawa, M. Suginome, Organometallics 2007, 26, 1291-1294, 10.1021/om0609867
- Ref. 10
- Convenient Preparation of Silylboranes M. Suginome, T. Matsuda, and Y. Ito, Organometallics 2000, 19, 4647-4649, 10.1021/om000254t
- Synthesis and Reactions of Cyclic Silylboranes M. Suginome, H. Noguch, T. Hasui, and M. Murakami, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn, 2005, 78, 323-326, 10.1246/bcsj.78.323
- Ref. 11
- Silylboranes Bearing Dialkylamino Groups on Silicon as Silylene Equivalents: Palladium-Catalyzed Regioselective Synthesis of 2,4-Disubstituted Siloles T. Ohmura, K. Masuda, M. Suginome, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 1526-1527, 10.1021/ja073896h